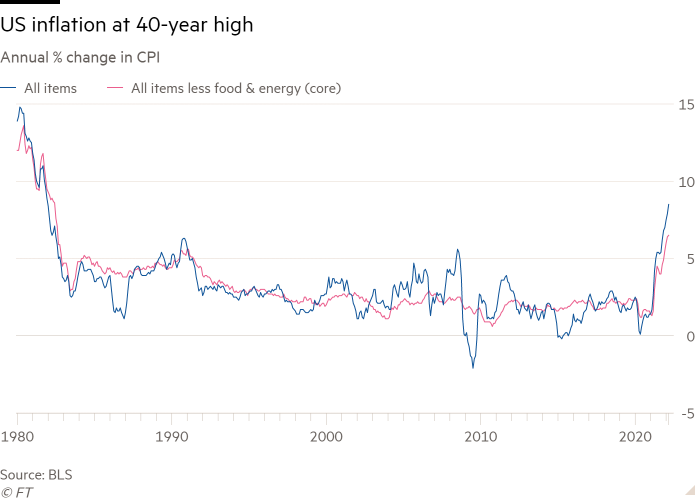
US client value progress surpassed 8 per cent in March, its quickest tempo since 1981 following a surge in the price of power and meals, sustaining strain on the Federal Reserve to take aggressive motion to deal with inflation.
The Shopper Value Index was 8.5 per cent final month in contrast with a 12 months in the past, marginally above Wall Road’s expectations, the Bureau of Labor Statistics stated on Tuesday. The month-to-month rise was 1.2 per cent, the quickest leap since September 2005 and a pointy acceleration from the 0.8 per cent improve recorded in February.
As soon as unstable objects reminiscent of meals and power are stripped out, “core” CPI superior 0.3 per cent in March. That was the slowest rise since September, however nonetheless translated to a 6.5 per cent annual improve.
Lael Brainard, a Fed governor awaiting Senate affirmation to be the following vice-chair, warned of “upside” dangers to inflation, citing Russia’s invasion of Ukraine — which is fuelling power and meals prices — and new Covid lockdowns in China that would worsen provide chain constraints.
“The economic system has sustained now numerous these sorts of inflationary shocks from exterior occasions,” she stated at a Wall Road Journal occasion. “We’ve seen lots of resilience however we’ve additionally seen very excessive inflation.”
It was the primary inflation studying that included a full month of the affect of the warfare in Ukraine, which has considerably clouded the worldwide outlook. Russia is among the world’s largest power exporters, and Russia and Ukraine are main suppliers of wheat and different grains.
The moderation in “core” CPI prompted a rally in Treasuries and in a single day funding markets, as merchants scaled again their bets for the tempo and measurement of rate of interest will increase this 12 months.
Nevertheless, markets are nonetheless pricing an increase within the Fed’s benchmark coverage fee to 2.45 per cent by the tip of 2022, down from 2.59 per cent earlier within the day however sharply increased than the present vary of 0.25 per cent to 0.50 per cent.
The Biden administration on Monday blamed surging costs on the warfare, with White Home press secretary Jen Psaki saying the CPI studying could be “terribly elevated resulting from Putin’s value hike”.
However Joe Manchin, the average Democratic senator from West Virginia, stated on Tuesday that it was a “disservice to the American individuals to behave as if inflation is a brand new phenomenon”.
Manchin, who has blocked Biden’s sweeping social spending plans on the grounds they had been inflationary, stated bringing costs “below management would require extra aggressive motion” from the Fed, in addition to a shift in power coverage on Capitol Hill.
“Everyone seems to be fearful about inflation,” stated Vincent Reinhart, a former senior Fed workers member who’s now chief economist at Mellon. “It’s primary within the polls. It’s consuming the Fed’s bandwidth proper now.”
The figures underscored the impact of unstable commodity costs, with a leap in petrol accounting for greater than half of the general improve in March CPI. Over the previous 12 months, costs on the pump have climbed 48 per cent, together with an 18.3 per cent rise between March and February.
Past power costs, core providers costs accelerated in March, up 0.6 per cent from the earlier month, or 4.7 per cent yearly. That’s the largest month-to-month leap since August 1992.
However there have been indicators that costs had been slowing elsewhere. Used automotive costs, which have been skyrocketing because the coronavirus pandemic pushed many Individuals away from mass transit, fell 3.8 per cent in March. The associated fee to purchase a brand new automobile rose 0.2 per cent from a month prior, a decrease improve than the achieve registered in February.
Considerations that inflation will develop into extra deeply entrenched on the planet’s largest economic system have prompted the US central financial institution in current weeks to imagine a extra aggressive strategy to tightening financial coverage.
The Fed is now poised to lift rates of interest by half a share level at its subsequent coverage assembly in Could, double the tempo of its March fee rise, because it seeks to raise its benchmark coverage fee to a extra “impartial” stage that neither aids nor constrains progress by the tip of the 12 months.
Officers forecast that fee to be roughly 2.4 per cent, implying at the very least yet another half-point adjustment along with 4 extra quarter-point fee rises in 2022.
The central financial institution can also be set to quickly start shrinking its $9tn steadiness sheet, constructing as much as as a lot as $95bn a month over roughly three months.
Brainard stated that course of would begin as early as June and, mixed with fee rises, ought to carry the Fed’s coverage to a extra impartial setting “over time”.
US monetary markets climbed on Tuesday, with the benchmark S&P 500 rising 0.5 per cent and the technology-heavy Nasdaq Composite advancing 0.8 per cent. US Treasuries additionally gained, with the yield on the 10-year notice falling practically 0.1 share factors to 2.68 per cent.