Did an worker go away your enterprise? It’s time to whip out your worker termination guidelines to see what you want to do. And one of many tasks on stated guidelines is giving terminated staff their last pay. However, how quickly do you want to pay it out? Cue last paycheck legal guidelines by state.
Learn on to study (and adjust to) last paycheck legal guidelines.
Normal guidelines for issuing termination pay
No matter whether or not you hearth an worker or they stop, you need to give them their final paycheck.
The ultimate paycheck ought to comprise the worker’s common wages from the newest pay interval, together with different sorts of compensation, similar to accrued trip, bonus, and fee pay.
You could possibly withhold cash from the worker’s final paycheck in the event that they owe your enterprise and you’ve got written authorization to take action. For instance, an worker should still owe you cash from a wage advance settlement. You’ll want to test along with your state earlier than doing this.
You can’t withhold unpaid wages that the worker earned, even in case you fired them. And, you can not connect a situation of receipt to the ultimate paycheck.
Though final paycheck legal guidelines fluctuate by state, giving a terminated worker their last paycheck on their final day can simplify your tasks. That manner, you don’t must mail the paycheck or have the worker choose it up from your enterprise at a later date.
Understand that the worker’s last paycheck isn’t the identical factor as severance pay. Severance pay is cash you give to an worker for a sure size of time after they lose their job. Not like a last paycheck, severance pay is negotiable. And, you might require staff to signal one thing saying they received’t sue your enterprise in the event that they settle for severance pay.
Remaining paycheck legal guidelines by state
There isn’t a federal last paycheck regulation that requires employers to offer staff their wages instantly. However, some states require the employer to offer a terminated worker’s last paycheck instantly or inside a sure timeframe, similar to the next payday. And in some states, the ultimate paycheck legal guidelines rely on whether or not the worker was fired or stop.

As an employer, you need to comply with your state’s last paycheck legal guidelines. Failing to take action may end up in penalties or perhaps a lawsuit. Past when the final paycheck is due, your state may set additional rules on issues like paying out unused trip pay.
Termination pay by state: Chart
Check out the next chart for final paycheck legal guidelines, for each staff who stop and staff you hearth. Understand that state legal guidelines can change, so test along with your state for extra info (utilizing the helpful hyperlinks supplied beneath!).
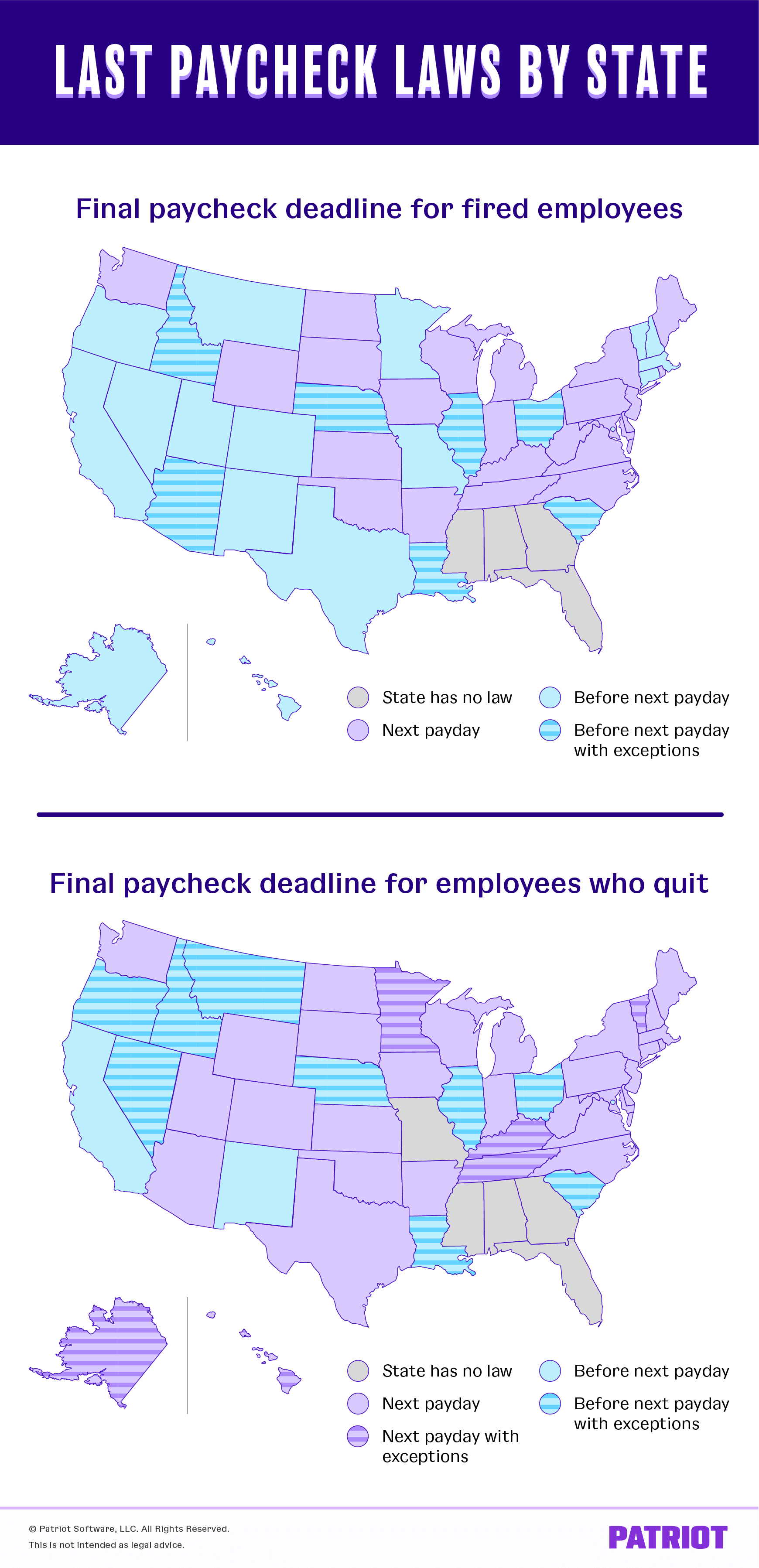
| State | Remaining Paycheck Deadline for Fired Staff | Remaining Paycheck Deadline for Staff Who Give up |
|---|---|---|
| Alabama | None | None |
| Alaska | 3 working days after the worker’s day of termination | Subsequent payday that’s not less than 3 working days after the worker’s final day |
| Arizona | 7 working days or the following common payday (whichever comes first) | Subsequent payday |
| Arkansas | Subsequent payday (employers owe double the wages due if wages are usually not paid inside 7 days of payday) | Subsequent payday |
| California | Instantly on the time of termination (with exceptions for seasonal staff in sure industries) | Instantly if the worker provides not less than 72 hours prior discover; 72 hours after quitting if the worker provides no discover |
| Colorado | Instantly (with some exceptions) | Subsequent payday |
| Connecticut | Subsequent enterprise day | Subsequent payday |
| D.C. | Subsequent working day | Subsequent payday or inside 7 days of resignation date, whichever is earlier |
| Delaware | Subsequent payday | Subsequent payday |
| Florida | None | None |
| Georgia | None | None |
| Hawaii | Instantly, or subsequent working day | Subsequent payday, or instantly if the worker gave not less than one pay interval’s advance discover |
| Idaho | Subsequent payday or 10 enterprise days, whichever is earlier | Subsequent payday or 10 enterprise days, whichever is earlier |
| Illinois | Instantly if potential, but when not, subsequent payday | Instantly if potential, but when not, subsequent payday |
| Indiana | Subsequent payday | Subsequent payday |
| Iowa | Subsequent payday | Subsequent payday |
| Kansas | Subsequent payday | Subsequent payday |
| Kentucky | Subsequent payday or 14 days, whichever is later | Subsequent payday or 14 days, whichever is later |
| Louisiana | Subsequent payday or 15 days after the discharge date, whichever is earlier | Subsequent payday or 15 days after the discharge date, whichever is earlier |
| Maine | Subsequent payday | Subsequent payday |
| Maryland | Subsequent payday | Subsequent payday |
| Massachusetts | Instantly (in most circumstances) | Subsequent payday |
| Michigan | Subsequent payday (with exceptions for sure industries) | Subsequent payday |
| Minnesota | Inside 24 hours of a written demand for fee | Subsequent payday. If the payday is inside 5 days of the final day of labor, employers have as much as 20 days. |
| Mississippi | None | None |
| Missouri | Instantly | None |
| Montana | Instantly inside 4 hours or finish of the enterprise day (whichever happens first) | Subsequent payday or 15 days, whichever is earlier |
| Nebraska | Subsequent payday or inside 2 weeks, whichever is earlier | Subsequent payday or inside 2 weeks, whichever is earlier |
| Nevada | Inside 3 days | Subsequent payday or inside 7 days, whichever is earlier |
| New Hampshire | Inside 72 hours | Subsequent payday |
| New Jersey | Subsequent payday | Subsequent payday |
| New Mexico | Inside 5 days; job, piece, and fee wages due inside 10 days | Inside 5 days; job, piece, and fee wages due inside 10 days |
| New York | Subsequent payday | Subsequent payday |
| North Carolina | Subsequent payday | Subsequent payday |
| North Dakota | Subsequent payday | Subsequent payday |
| Ohio | Subsequent payday or inside 15 days, whichever is earlier | Subsequent payday or inside 15 days, whichever is earlier |
| Oklahoma | Subsequent payday | Subsequent payday |
| Oregon | Subsequent enterprise day | On the final day of employment if the worker gave 48 hours discover; inside 5 working days or the following payday (whichever comes first) if staff didn’t give 48 hours discover |
| Pennsylvania | Subsequent payday | Subsequent payday |
| Rhode Island | Subsequent payday | Subsequent payday |
| South Carolina | Inside 48 hours or subsequent payday, not exceeding 30 days | Inside 48 hours or subsequent payday, not exceeding 30 days |
| South Dakota | Subsequent payday | Subsequent payday |
| Tennessee | Subsequent payday or inside 21 days, whichever happens final | Subsequent payday or inside 21 days, whichever happens final |
| Texas | Inside 6 calendar days | Subsequent payday |
| Utah | Inside 24 hours | Subsequent payday |
| Vermont | Inside 72 hours | Subsequent payday or the next Friday |
| Virginia | Subsequent payday | Subsequent payday |
| Washington | Subsequent payday | Subsequent payday |
| West Virginia | Subsequent payday | Subsequent payday |
| Wisconsin | Subsequent payday | Subsequent payday |
| Wyoming | Subsequent payday | Subsequent payday |
Make sure that to seek the advice of your state authorities for extra info. Your state may:
- Have extra restrictive last paycheck legal guidelines for some circumstances
- Make exceptions when you’ve got a written contract or settlement with an worker
- Let staff request earlier fee
Remaining pay by state: Map
Use our quick-reference map to search out your state’s last paycheck legal guidelines.
Searching for a simple option to run payroll? Patriot’s on-line payroll software program enables you to run payroll utilizing a easy three-step course of. And, we provide free setup and assist. Get your free trial now!
This text has been up to date from its unique publication date of October 15, 2018.
This isn’t supposed as authorized recommendation; for extra info, please click on right here.
