Welcome to Perceptron, TechCrunch’s weekly roundup of AI information and analysis from around the globe. Machine studying is a key expertise in virtually each trade now, and there’s far an excessive amount of occurring for anybody to maintain up with all of it. This column goals to gather a number of the most fascinating current discoveries and papers within the subject of synthetic intelligence — and clarify why they matter.
(Previously referred to as Deep Science; try earlier editions right here.)
This week’s roundup begins with a pair of forward-thinking research from Fb/Meta. The primary is a collaboration with the College of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign that goals at decreasing the quantity of emissions from concrete manufacturing. Concrete accounts for some 8 p.c of carbon emissions, so even a small enchancment might assist us meet local weather targets.
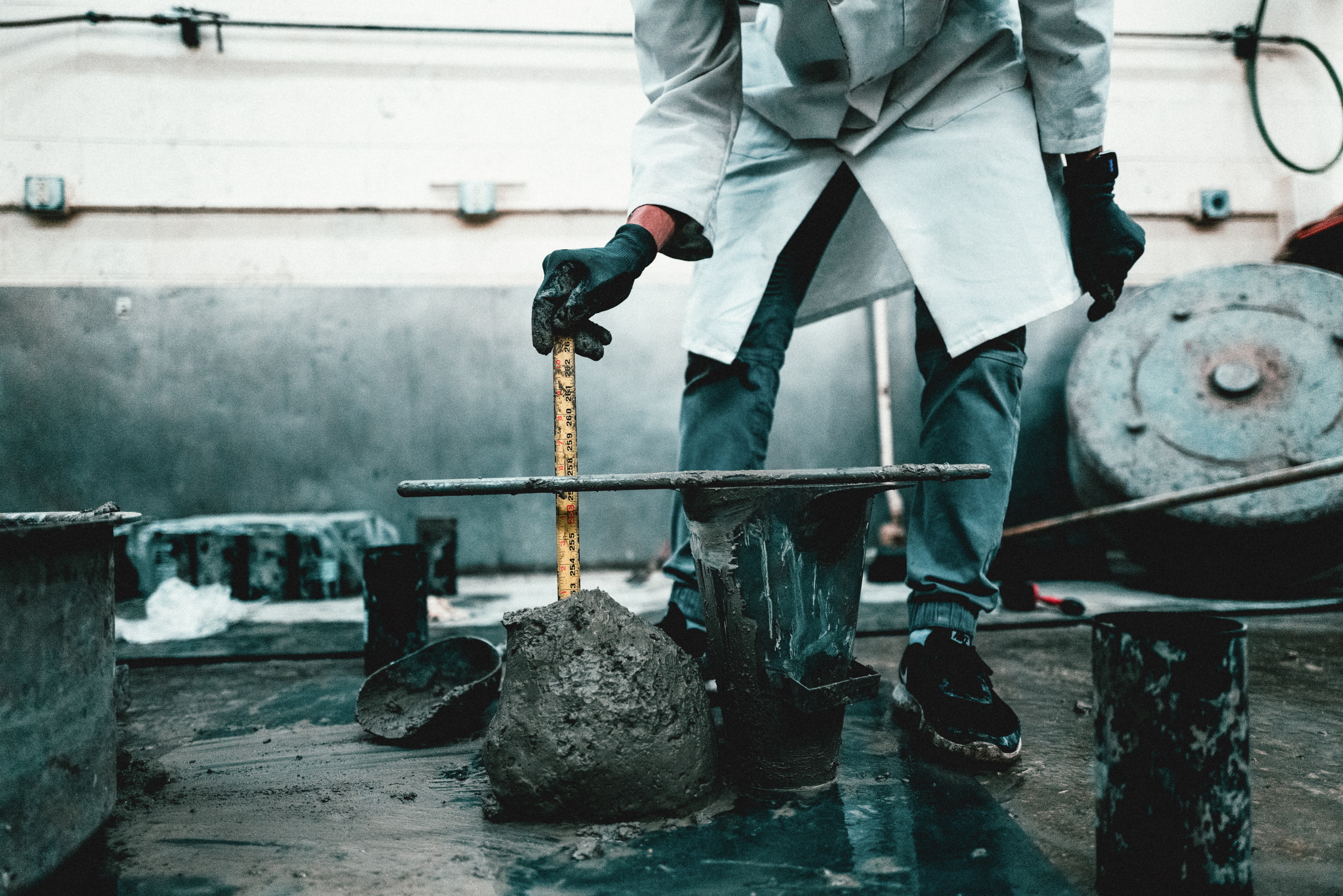

That is referred to as “droop testing.”
What the Meta/UIUC staff did was practice a mannequin on over a thousand concrete formulation, which differed in proportions of sand, slag, floor glass, and different supplies (you’ll be able to see a pattern chunk of extra photogenic concrete up prime). Discovering the delicate tendencies on this dataset, it was capable of output a lot of newformulas optimizing for each power and low emissions. The profitable components turned out to have 40 p.c much less emissions than the regional normal, and met… nicely, some of the power necessities. It’s extraordinarily promising, and follow-up research within the subject ought to transfer the ball once more quickly.
The second Meta research has to do with altering how language fashions work. The corporate desires to work with neural imaging specialists and different researchers to check how language fashions evaluate to precise mind exercise throughout comparable duties.
Specifically, they’re within the human functionality of anticipating phrases far forward of the present one whereas talking or listening — like realizing a sentence will finish in a sure means, or that there’s a “however” coming. AI fashions are getting superb, however they nonetheless primarily work by including phrases one after the other like Lego bricks, often trying backwards to see if it is smart. They’re simply getting began however they have already got some fascinating outcomes.
Again on the supplies tip, researchers at Oak Ridge Nationwide Lab are getting in on the AI formulation enjoyable. Utilizing a dataset of quantum chemistry calculations, no matter these are, the staff created a neural community that would predict materials properties — however then inverted it in order that they may enter properties and have it recommend supplies.
“As an alternative of taking a fabric and predicting its given properties, we wished to decide on the best properties for our goal and work backward to design for these properties rapidly and effectively with a excessive diploma of confidence. That’s referred to as inverse design,” stated ORNL’s Victor Fung. It appears to have labored — however you’ll be able to test for your self by operating the code on Github.
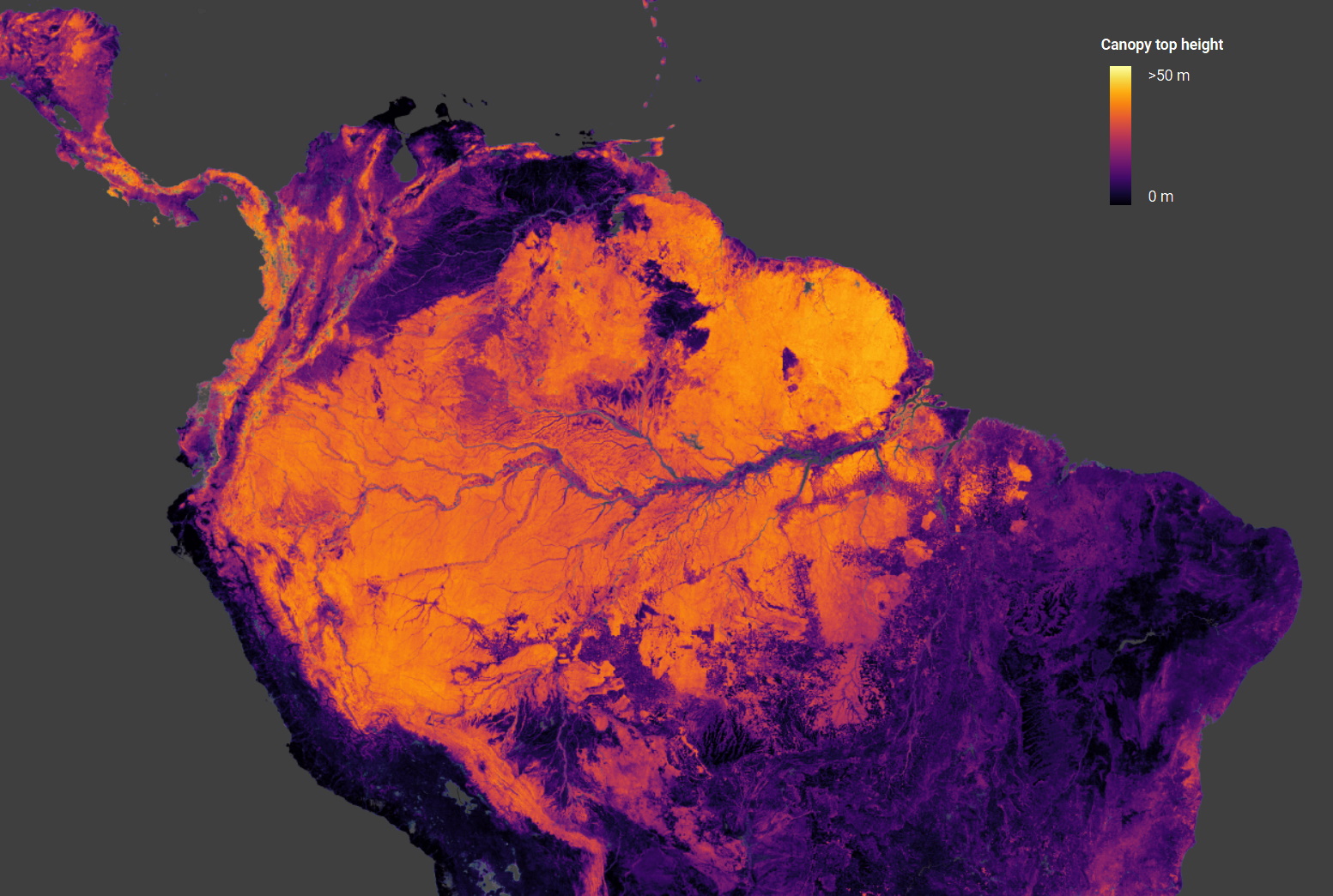
Picture Credit: ETHZ
Involved with bodily predictions on a wholly completely different scale, this ETHZ challenge estimates the heights of tree canopies across the globe utilizing knowledge from ESA’s Copernicus Sentinel-2 satellites (for optical imagery) and NASA’s GEDI (orbital laser ranging). Combining the 2 in a convolutional neural community leads to an correct world map of tree heights as much as 55 meters tall.
Having the ability to do this type of common survey of biomass at a world scale is necessary for local weather monitoring, as NASA’s Ralph Dubayah explains: “We merely have no idea how tall timber are globally. We want good world maps of the place timber are. As a result of each time we reduce down timber, we launch carbon into the environment, and we don’t know the way a lot carbon we’re releasing.”
You possibly can simply browse the info in map type right here.
Additionally pertaining to landscapes is that this DARPA challenge all about creating extraordinarily large-scale simulated environments for digital autonomous automobiles to traverse. They awarded the contract to Intel, although they could have saved some cash by contacting the makers of the sport Snowrunner, which principally does what DARPA desires for $30.

Picture Credit: Intel
The aim of RACER-Sim is to develop off-road AVs that already know what it’s wish to rumble over a rocky desert and different harsh terrain. The 4-year program will focus first on creating the environments, constructing fashions within the simulator, then in a while transferring the talents to bodily robotic techniques.
Within the area of AI prescription drugs, which has about 500 completely different corporations proper now, MIT has a sane method in a mannequin that solely suggests molecules that may really be made. “Fashions usually recommend new molecular buildings which are troublesome or inconceivable to provide in a laboratory. If a chemist can’t really make the molecule, its disease-fighting properties can’t be examined.”
Seems cool, however are you able to make it with out powdered unicorn horn?
The MIT mannequin “ensures that molecules are composed of supplies that may be bought and that the chemical reactions that happen between these supplies observe the legal guidelines of chemistry.” It form of seems like what Molecule.one does, however built-in into the invention course of. It actually could be good to know that the miracle drug your AI is proposing doesn’t require any fairy mud or different unique matter.
One other bit of labor from MIT, the College of Washington, and others is about educating robots to work together with on a regular basis objects — one thing all of us hope turns into commonplace within the subsequent couple many years, since a few of us don’t have dishwashers. The issue is that it’s very troublesome to inform precisely how folks work together with objects, since we will’t relay our knowledge in excessive constancy to coach a mannequin with. So there’s a number of knowledge annotation and guide labeling concerned.
The brand new method focuses on observing and inferring 3D geometry very intently in order that it solely takes a couple of examples of an individual greedy an object for the system to learn to do it itself. Usually it’d take lots of of examples or hundreds of repetitions in a simulator, however this one wanted simply 10 human demonstrations per object with a purpose to successfully manipulate that object.
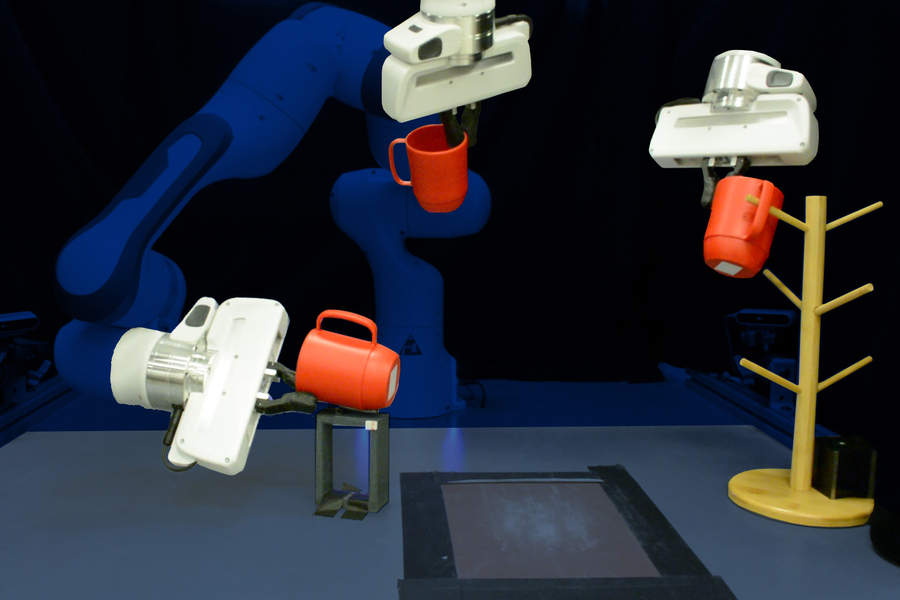

Picture Credit: MIT
It achieved an 85 p.c success charge with this minimal coaching, means higher than the baseline mannequin. It’s presently restricted to a handful of classes however the researchers hope it may be generalized.
Final up this week is a few promising work from Deepmind on a multimodal “visible language mannequin” that mixes visible information with linguistic information in order that concepts like “three cats sitting on a fence” have a type of crossover illustration between grammar and imagery. That’s the way in which our personal minds work, in any case.
Flamingo, their new “basic goal” mannequin, can do visible identification but additionally interact in dialogue, not as a result of it’s two fashions in a single however as a result of it marries language and visible understanding collectively. As we’ve seen from different analysis organizations, this type of multimodal method produces good outcomes however continues to be extremely experimental and computationally intense.